Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) like GPT-4V and Gemini promise powerful vision-language understanding—but how well do they actually read text in images? Despite their general capabilities, their performance on optical character recognition (OCR) tasks is often inconsistent, especially with handwritten notes, non-Latin scripts, dense receipts, or mathematical expressions. Without a standardized way to measure this, teams risk deploying models that fail silently on critical visual text.
Enter OCRBench: the first comprehensive, open-source evaluation benchmark specifically designed to uncover the true OCR strengths and weaknesses of large multimodal models. Backed by rigorous human-verified data and covering 29 diverse datasets across five core OCR-related tasks, OCRBench provides an actionable, reproducible framework for technical teams to make informed decisions—before committing to a model in production.
Why Standardized OCR Evaluation Matters
Many LMMs claim strong multimodal abilities, but “vision-language understanding” doesn’t automatically translate to reliable text extraction. In real-world applications—such as parsing invoices, interpreting street signs in foreign languages, or digitizing handwritten forms—even minor OCR failures can cascade into major errors.
Prior to OCRBench, there was no unified benchmark to systematically test how models perform across:
- Low-quality or distorted text
- Handwritten content
- Multilingual or non-Latin scripts
- Structured documents vs. unstructured scenes
- Symbolic notations like mathematical formulas
OCRBench closes this gap by offering a standardized, modular, and extensible testbed that reflects actual deployment challenges—not just idealized lab conditions.
Core Components and Capabilities
OCRBench evaluates models across five key dimensions:
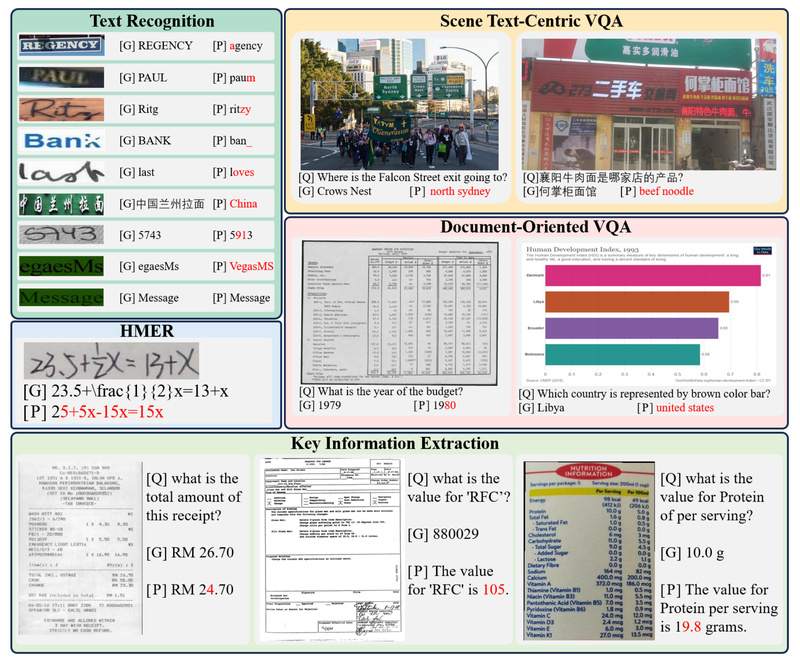
1. Text Recognition
Basic character recognition across printed and scene text, including challenging fonts, orientations, and lighting conditions.
2. Scene Text-Centric Visual Question Answering (VQA)
Questions that require reading and reasoning about text in natural scenes—e.g., “What is the name of the restaurant on this storefront?”
3. Document-Oriented VQA
Tasks involving structured documents like forms, reports, or tables—e.g., “What is the invoice total?”
4. Key Information Extraction (KIE)
Extracting structured fields from semi-structured documents such as receipts, ID cards, or shipping labels.
5. Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition (HMER)
Decoding complex handwritten equations—a notoriously difficult task even for specialized OCR systems.
All 1,000+ question-answer pairs in the original OCRBench are manually verified for accuracy, ensuring high-fidelity evaluation.
OCRBench v2: A Major Leap Forward
Released in late 2024, OCRBench v2 dramatically expands scope and difficulty:
- 31 real-world scenarios, including diagrams, dense text regions (via DTVQA), receipts, street signs, and scientific formulas
- Over 10,000 human-verified bilingual (English/Chinese) QA pairs
- 4× more tasks than the original benchmark
- Enhanced support for non-semantic text, low-resource scripts, and handwriting variability
This makes OCRBench v2 not just a benchmark—but a stress test for real-world robustness.
Practical Use Cases for Teams and Researchers
OCRBench is invaluable when you need to:
- Compare off-the-shelf LMMs (e.g., GPT-4V vs. Gemini vs. open-source alternatives) for a document-processing pipeline
- Validate zero-shot OCR performance without costly fine-tuning
- Assess multilingual support before launching a global product
- Benchmark your own model against community standards using reproducible metrics
- Identify failure modes in handwriting or symbol-heavy domains (e.g., education, scientific publishing, logistics)
For example, a fintech startup evaluating receipt-scanning capabilities can use OCRBench’s KIE and Document VQA components to quantify accuracy across vendors—before writing a single line of integration code.
How to Get Started
OCRBench is open-source and designed for immediate use:
- GitHub repository: https://github.com/Yuliang-Liu/MultimodalOCR
- Framework integrations: Native support in popular evaluation suites like VLMEvalKit and lmms-eval
- Modular design: Run specific task suites (e.g., only HMER) or the full benchmark
- Evaluation pipeline included: Pre-processed datasets, scoring logic, and result aggregation tools are provided
You can evaluate both local models and cloud APIs using the same standardized protocol—enabling fair, apples-to-apples comparisons.
Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, OCRBench is an evaluation tool, not an OCR engine. It measures performance—it doesn’t perform recognition itself.
Also note:
- Language coverage, while expanded in v2, still focuses primarily on English and Chinese; coverage for very low-resource scripts (e.g., Indigenous or historic scripts) may be limited
- Some private datasets in OCRBench v2 require access requests for licensing reasons
- The benchmark emphasizes zero-shot or few-shot evaluation—it’s not designed for fine-tuning workflows
These boundaries ensure OCRBench remains focused, rigorous, and ethically compliant.
Summary
OCRBench solves a critical problem: the lack of transparency around how well large multimodal models actually read text in the real world. By offering a standardized, human-verified, and scenario-rich evaluation framework, it empowers engineers, researchers, and product teams to cut through marketing claims and make data-driven decisions. Whether you’re building a multilingual visual assistant, automating document workflows, or pushing the limits of zero-shot reasoning, OCRBench gives you the ground truth you need—before deployment.
With active updates, community integrations, and the expanded OCRBench v2, it’s quickly becoming the gold standard for OCR evaluation in the age of multimodal AI.