As large language models (LLMs) become deeply embedded in enterprise workflows, content platforms, and research pipelines, the ability to verify whether a piece of text was generated by an AI—and by which model—has become increasingly critical. From preventing academic dishonesty to ensuring compliance in regulated industries, the need for reliable, imperceptible, and algorithmically detectable signals in AI output is no longer optional. Enter MarkLLM, an open-source Python toolkit that standardizes the implementation, analysis, and evaluation of LLM watermarking techniques under one unified, extensible framework.
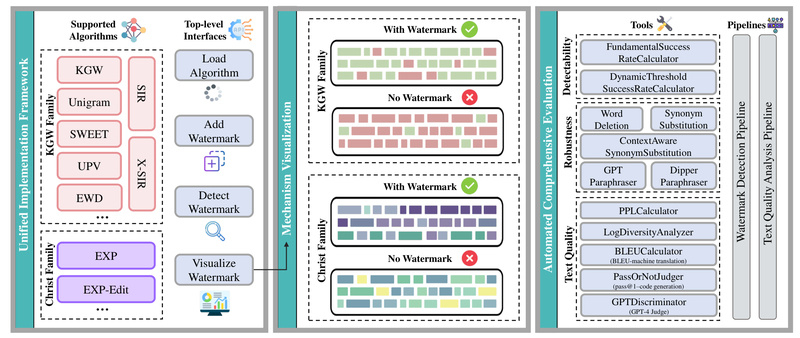
MarkLLM addresses a major pain point: the fragmentation and complexity of existing watermarking algorithms. With dozens of methods published across top-tier conferences—each with unique assumptions, hyperparameters, and evaluation protocols—researchers and engineering teams often face steep learning curves just to compare or deploy them. MarkLLM eliminates this friction by providing plug-and-play support for over 18 state-of-the-art watermarking approaches, automated evaluation pipelines, and intuitive visualization utilities that reveal how watermarks operate under the hood—all accessible through clean, high-level APIs.
A Unified Platform for Watermark Implementation and Experimentation
MarkLLM’s core innovation lies in its modular design. Rather than requiring users to reimplement algorithms from scratch or adapt incompatible codebases, the toolkit offers a standardized interface via AutoWatermark.load(). This single entry point lets users instantiate any supported method—such as KGW (ICML 2023), SynthID-Text (Nature 2024), or Adaptive Watermark (ICML 2024)—with just a configuration file and a compatible LLM (e.g., OPT, Llama).
Under the hood, MarkLLM abstracts away low-level details like token hashing, probability redistribution, or semantic embedding alignment. This enables practitioners—whether NLP engineers, compliance officers, or academic researchers—to focus on evaluating watermark behavior in real-world contexts rather than debugging cryptographic pseudo-random functions.
Transparent Mechanisms Through Built-in Visualization
One of the biggest barriers to trust in watermarking is opacity: how can you verify a signal is truly embedded if you can’t see it? MarkLLM directly tackles this by offering algorithm-specific visualization tools that render watermark influence at the token level.
For discrete watermark families like KGW, the DiscreteVisualizer color-codes tokens based on whether they belong to a green-list (favored) or red-list (suppressed) set. For continuous methods like EXP or Unbiased Watermark, the ContinuousVisualizer displays per-token logit perturbations or sampling biases as a gradient heatmap overlaid on the generated text. These visualizations not only aid debugging but also serve as compelling explanatory artifacts for stakeholders unfamiliar with watermark internals.
Rigorous, Multi-Dimensional Evaluation Out of the Box
MarkLLM goes beyond generation and detection by offering a comprehensive evaluation suite comprising 12 tools across three key dimensions:
- Detectability: Measures how reliably watermarks can be identified using statistical tests (e.g., G-test, LLR scores).
- Robustness: Evaluates resilience against attacks like word deletion, synonym substitution, GPT-4 paraphrasing, and back-translation.
- Text Quality Impact: Quantifies degradation via perplexity (PPL), lexical diversity, BLEU scores, and LLM-based fluency judges.
Two automated pipeline types—DetectionPipeline and QualityAnalysisPipeline—allow users to run end-to-end benchmarks with minimal code. For example, comparing KGW’s performance before and after a 30% word deletion attack requires only a few lines of configuration. This enables rapid, reproducible benchmarking across algorithms and threat models.
Practical Use Cases for Decision-Makers
MarkLLM delivers immediate value in several real-world scenarios:
- Enterprise AI Governance: R&D teams can watermark internal LLM outputs to track unauthorized redistribution or exfiltration.
- Content Moderation Platforms: User-submitted essays, reviews, or reports can be screened for AI origin using standardized detectors.
- Academic Research: Scholars can fairly compare novel watermarking methods against established baselines under identical evaluation conditions.
- Compliance Engineering: Developers building AI disclosure features can integrate watermarked generation directly into application backends.
Because MarkLLM supports integration with popular inference frameworks (e.g., vLLM via MarkvLLM_demo.py), adoption doesn’t require overhauling existing deployment stacks.
Getting Started in Minutes
Installation is straightforward:
pip install markllm
Core usage involves three steps:
- Load a pre-trained LLM and tokenizer into a
TransformersConfigobject. - Instantiate a watermark algorithm using
AutoWatermark.load(). - Generate watermarked text and run detection or quality analysis.
Example scripts, Jupyter notebooks (MarkLLM_demo.ipynb), and test cases in the evaluation/examples/ directory provide ready-to-run templates for common tasks—from basic generation to adversarial robustness testing.
Note: Some algorithms (e.g., DiPmark, SIR) rely on auxiliary models stored in the team’s Hugging Face repository Generative-Watermark-Toolkits. Users must download these weights into the local
model/directory before execution, as detailed in the project’s README.
Limitations and Considerations
While MarkLLM significantly lowers the barrier to watermark experimentation, users should be aware of key constraints:
- Algorithm-specific trade-offs: Some methods (e.g., SynthID-Text) offer high robustness but require fine-tuned generator models; others (e.g., KGW) are lightweight but vulnerable to paraphrasing.
- Attack resilience isn’t absolute: No watermark survives arbitrary, semantics-preserving rewrites by powerful LLMs—MarkLLM includes tools to measure how much degradation occurs, not guarantee invincibility.
- Text-only focus: MarkLLM targets natural language; multimodal watermarking (e.g., for images) is handled by the team’s separate MarkDiffusion toolkit.
- Resource demands: Evaluation pipelines may require additional GPUs or large language models for quality scoring (e.g., Llama-7B for PPL).
These limitations are transparently documented, and the toolkit’s modular design allows users to assess them empirically in their own contexts.
Summary
MarkLLM democratizes access to LLM watermarking by unifying fragmented research into a single, well-documented, and extensible platform. It empowers technical decision-makers to rapidly prototype, visualize, and evaluate watermarking strategies—without needing cryptography expertise or months of implementation effort. In an era where AI-generated text is ubiquitous but unverified, MarkLLM provides a practical path toward accountable, traceable, and trustworthy language model deployment. For teams serious about AI provenance, it’s not just a toolkit—it’s a necessity.