OpenOCR is a general-purpose optical character recognition (OCR) system developed by the FVL Laboratory at Fudan University. Designed with both accuracy and efficiency as core principles, OpenOCR delivers state-of-the-art performance for scene text detection and recognition—particularly for English and Chinese content. Built on cutting-edge research like SVTRv2 and the instruction-guided IGTR framework, it offers a practical, production-ready solution for engineers, researchers, and technical decision-makers seeking reliable OCR without unnecessary complexity.
Unlike many academic prototypes that prioritize novelty over deployability, OpenOCR is engineered for real-world use. It supports both server-grade and mobile-optimized models, provides seamless ONNX export for cross-platform compatibility, and enables fine-tuning on custom datasets—making it adaptable to domain-specific needs while maintaining fast inference speeds.
Why OpenOCR Stands Out
Backed by Peer-Reviewed Innovation
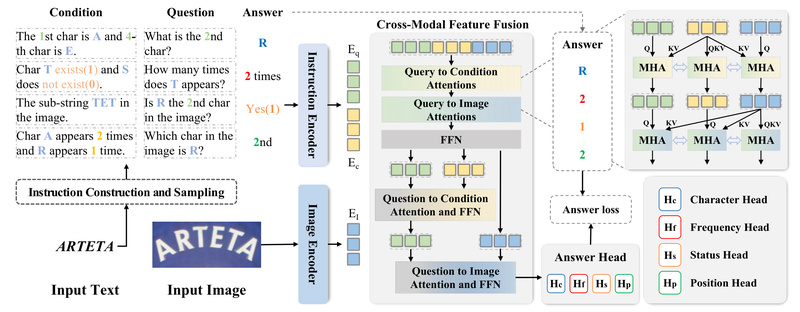
At the heart of OpenOCR lies a suite of rigorously evaluated algorithms. Notably, its recognition module leverages SVTRv2, a model that demonstrates how Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) can outperform traditional encoder-decoder architectures in both accuracy and speed on real-world text. Additionally, the Instruction-Guided Scene Text Recognition (IGTR) paradigm—published in TPAMI 2025—reimagines text recognition as a character-level reasoning task via instruction-based question answering. This approach significantly improves handling of rare or visually similar characters, a persistent challenge in OCR.
Proven Performance Gains
OpenOCR has been benchmarked against industry standards like PP-OCRv4. On official OCR competition leaderboards, it achieves a 4.5% higher accuracy while maintaining comparable inference speed. This balance of precision and efficiency makes it especially valuable in latency-sensitive or high-throughput environments such as document processing pipelines or mobile scanning apps.
Practical Design for Real Deployment
OpenOCR isn’t just a research artifact—it’s built for integration:
- Supports both English and Chinese text detection and recognition.
- Offers two model variants: a server model for maximum accuracy and a lightweight mobile model for edge devices.
- Provides ONNX export, enabling deployment across diverse runtimes (e.g., ONNX Runtime, TensorRT) without PyTorch dependencies.
- Includes ready-to-use Python APIs for rapid prototyping and production use.
Ideal Use Cases
OpenOCR excels in scenarios where robust, multilingual OCR is required with minimal overhead:
- Document digitization: Accurately extract text from scanned forms, contracts, or academic papers containing mixed English and Chinese content.
- Receipt and invoice processing: Automate data entry from retail or financial documents in international business contexts.
- Educational technology: Power apps that convert textbook images or handwritten notes into editable text for learning aids.
- Enterprise automation: Integrate into internal tools for converting legacy image-based records into structured data.
Its strong performance on real-world (not just synthetic) datasets—thanks to training on Union14M-L-Filter—ensures reliability in noisy, low-quality, or irregularly formatted inputs commonly encountered outside controlled environments.
Getting Started Is Simple
OpenOCR supports two inference backends, allowing users to choose based on their infrastructure:
Option 1: ONNX Runtime (Lightweight, No PyTorch)
pip install openocr-python onnxruntime
from openocr import OpenOCR
engine = OpenCSR(backend='onnx', device='cpu')
result, _ = engine('/path/to/your/image.jpg')
Option 2: PyTorch (For Training or Advanced Control)
After installing PyTorch ≥1.13, simply run:
pip install openocr-python from openocr import OpenOCR engine = OpenOCR() # defaults to PyTorch backend result, _ = engine(['/folder/of/images', 'single_image.png'])
For interactive exploration, a local Gradio demo is included—ideal for quick validation before integration.
Flexibility for Custom Needs
While OpenOCR works out-of-the-box, it also supports customization:
- Fine-tune detection or recognition models on your own labeled dataset using provided scripts.
- Export trained models to ONNX, ensuring compatibility with edge devices or cloud inference services that don’t support PyTorch.
This makes OpenOCR suitable not only for general-purpose use but also for specialized domains like medical forms, industrial labels, or historical document archives—provided the text falls within supported scripts.
Limitations to Consider
OpenOCR is not a universal OCR solution for all languages or scripts. Currently, it focuses on English and Chinese, with no built-in support for Arabic, Devanagari, or other non-Latin/Chinese writing systems.
Additionally, while the recognition component is mature and benchmarked, the scene text detection module is still under active development, as noted in the project’s reproduction roadmap. Users requiring end-to-end text spotting should verify detection performance on their specific data or consider integrating OpenOCR’s recognizer with an external detector.
Performance also depends on input image quality: blurry, low-resolution, or heavily distorted text may reduce accuracy, as with most OCR systems.
Summary
OpenOCR delivers a rare combination: research-grade accuracy grounded in peer-reviewed methods like IGTR and SVTRv2, paired with production-ready features like ONNX export, multilingual support, and easy fine-tuning. For practitioners evaluating OCR systems for English-Chinese applications, it offers a compelling balance of performance, speed, and deployability—without the bloat or instability of experimental frameworks. If your project demands reliable, efficient, and adaptable OCR for real-world text, OpenOCR is a strong, future-ready choice worth adopting today.