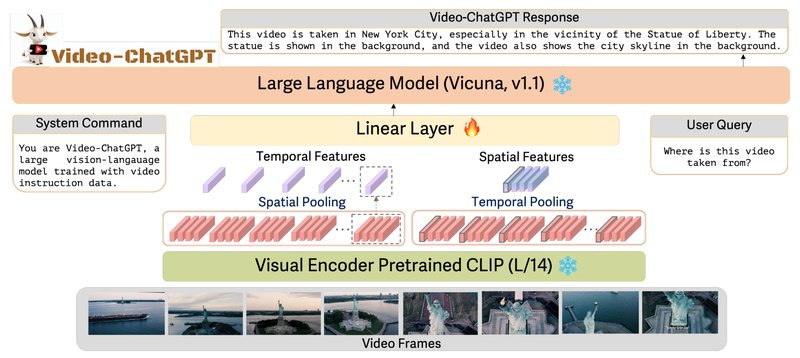
Video-ChatGPT is a state-of-the-art multimodal AI system that bridges the gap between video content and human-like conversation. Built by researchers at Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI), it integrates a video-adapted visual encoder with a powerful large language model (LLM) to enable natural, detailed, and temporally aware dialogue about videos. Unlike traditional image-based models, Video-ChatGPT is specifically designed to capture both spatial and temporal dynamics in video, making it uniquely capable of answering complex questions, generating descriptive narratives, and reasoning over actions across time.
Whether you’re building intelligent tutoring systems, accessibility tools, or AI agents for video analytics, Video-ChatGPT offers a robust, open-source foundation that has already demonstrated superior performance across multiple benchmarks.
Why Video-ChatGPT Stands Out
Trained on a Scalable, High-Quality Video Instruction Dataset
At the core of Video-ChatGPT is the VideoInstruct-100K dataset—a collection of 100,000 video-instruction pairs created through a hybrid human-assisted and semi-automated pipeline. This approach ensures data diversity, label robustness, and scalability, covering a wide range of video categories including sports, cooking, daily activities, and more. The instructions are designed to elicit detailed, video-specific responses, enabling the model to learn nuanced reasoning about motion, causality, object interactions, and temporal sequences.
State-of-the-Art Performance on Video QA Benchmarks
Video-ChatGPT consistently outperforms competing models like Video LLaMA, LLaMA Adapter, and Video Chat across major zero-shot video question-answering benchmarks:
- MSVD-QA: 64.9% accuracy (vs. 56.3% for Video Chat)
- MSRVTT-QA: 49.3% accuracy
- TGIF-QA: 51.4% accuracy
- ActivityNet-QA: 35.2% accuracy
These results reflect not only factual correctness but also the model’s ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant answers without task-specific fine-tuning.
Superior Qualitative Capabilities
Beyond benchmark scores, Video-ChatGPT excels in human-evaluated dimensions critical for real-world applications:
- Correctness of Information: 2.40/3.0
- Detail Orientation: 2.52/3.0
- Contextual Understanding: 2.62/3.0
- Consistency: 2.37/3.0
It particularly shines in tasks requiring temporal reasoning (e.g., “What happened before the person opened the door?”) and spatial understanding (e.g., “Where is the cat relative to the sofa?”), making it suitable for applications where precision and coherence matter.
First Dedicated Evaluation Framework for Video Dialogue
Recognizing the lack of standardized metrics for video-based conversational models, the team behind Video-ChatGPT introduced VCGBench-Diverse—a comprehensive benchmark with 4,354 human-annotated QA pairs across 18 video categories. This framework enables objective, fine-grained evaluation of correctness, creativity, action recognition, and temporal coherence, setting a new standard for future research and development.
Practical Use Cases for Developers and Product Teams
Video-ChatGPT isn’t just a research prototype—it’s engineered for real-world deployment in scenarios where understanding video content through conversation adds tangible value:
- Educational Assistants: Help students understand lecture videos, lab demonstrations, or historical footage by answering questions in natural language.
- Accessibility Tools: Provide verbal descriptions of video content for visually impaired users, going beyond simple object detection to explain actions and sequences.
- Customer Support Automation: Enable bots to interpret tutorial or troubleshooting videos and respond to user queries like “Why did the software freeze at 2:15?”
- Sports & Surveillance Analytics: Support analysts by generating summaries (“The player dribbled past two defenders before scoring”) or answering forensic questions (“When did the package arrive?”).
Its strong zero-shot capabilities mean many of these applications can be prototyped quickly without extensive retraining.
Getting Started Is Straightforward
The Video-ChatGPT codebase is well-documented and designed for engineers and researchers alike:
- Set up the environment using Conda and Python 3.10.
- Clone the repository and install dependencies, including optional acceleration libraries like FlashAttention for training.
- Run the offline demo with your own videos to test inference capabilities.
- Explore training scripts and the VideoInstruct-100K dataset if you need to adapt the model to a specific domain.
An online demo is also available for immediate experimentation, allowing you to upload videos and interact with the model in real time.
Important Considerations
While Video-ChatGPT is powerful, it’s important to understand its scope and constraints:
- Not a video generator: It understands and converses about videos but cannot generate, edit, or synthesize video content.
- Compute requirements: Inference runs on standard GPUs, but training demands significant resources (e.g., multi-GPU setups and FlashAttention support).
- License restrictions: The project is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0), meaning commercial use requires explicit permission.
- Domain adaptation: While strong in zero-shot settings, specialized domains (e.g., medical or industrial video) may benefit from fine-tuning using the provided training pipeline.
Summary
Video-ChatGPT represents a significant leap forward in video-language AI, combining large language models with spatiotemporal visual understanding to deliver accurate, detailed, and temporally coherent conversations about videos. Backed by a high-quality instruction dataset, a novel evaluation framework, and demonstrated superiority over existing models, it offers a compelling solution for developers, researchers, and product teams working on video understanding, accessibility, education, or analytics. With open-source code, clear documentation, and both online and offline demos, getting started has never been easier—for research, learning, or non-commercial innovation.