If you’ve ever tried building a natural language interface to a relational database, you know the real bottleneck isn’t the idea—it’s execution. Turning free-form English questions into correct, executable SQL is notoriously hard, especially across diverse schemas and complex query patterns. While large language models (LLMs) have made impressive strides in this space, most open tools either rely on prompt engineering (which often fails on harder queries) or require massive compute to fine-tune models effectively.
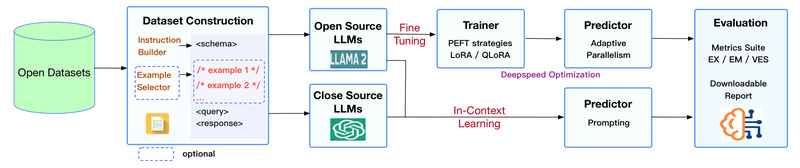
Enter DB-GPT-Hub: an open, modular benchmarking platform designed specifically for fine-tuning LLMs on Text-to-SQL tasks. Unlike black-box APIs or research-only frameworks, DB-GPT-Hub lowers the barrier to entry by providing standardized workflows, support for efficient tuning methods like LoRA and QLoRA, and compatibility with major open-source models—all while running on modest hardware. For technical decision-makers evaluating tools for data access, automation, or AI-augmented analytics, DB-GPT-Hub offers a rare combination of reproducibility, flexibility, and real-world practicality.
Why Fine-Tuning Matters for Text-to-SQL
Prompt-based approaches (e.g., zero-shot or few-shot inference with models like GPT-4) work well for simple queries but often falter on multi-table joins, nested subqueries, or domain-specific terminology. In contrast, supervised fine-tuning (SFT) adapts the model directly to the syntactic and semantic patterns of SQL, dramatically improving accuracy—especially on “Hard” and “Extra” difficulty examples from benchmarks like Spider.
However, full fine-tuning of billion-parameter models is prohibitively expensive. DB-GPT-Hub solves this by focusing on parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) techniques. Using LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) or its quantized variant QLoRA, you can tune 7B–13B models with as little as 6GB of GPU memory, making high-accuracy Text-to-SQL accessible to teams without cloud-scale budgets.
Key Capabilities That Accelerate Development
DB-GPT-Hub isn’t just another fine-tuning script—it’s a complete, standardized pipeline for building and evaluating database-aware LLMs.
Broad Model Support Out of the Box
The platform natively supports a wide range of leading open-source LLMs, including:
- CodeLlama (7B/13B)
- Llama2 and Llama3
- Qwen (7B/14B)
- Baichuan2 (7B/13B)
- ChatGLM3-6B
- Falcon, XVERSE, InternLM, and specialized SQL models like sqlcoder-7b
Each model comes with pre-configured settings for LoRA targets (e.g., q_proj,v_proj for Llama-family models) and prompt templates (llama2, chatml, etc.), eliminating hours of trial-and-error.
Unified Data Handling Across Benchmarks
DB-GPT-Hub includes built-in preprocessing for all major Text-to-SQL datasets:
- Spider: Cross-domain, single-turn queries (the de facto standard)
- BIRD-SQL: Real-world-scale databases with messy values and external knowledge needs
- CoSQL and SParC: Multi-turn, conversational query scenarios
- WikiSQL and CHASE: Simpler or Chinese-language alternatives
The data pipeline automatically fuses table schemas, foreign key relationships, and natural language instructions into a single input prompt—exactly how modern SFT methods expect context to be structured.
Built-In Evaluation with Execution Accuracy (EX)
Many Text-to-SQL tools report syntactic correctness, but execution accuracy (EX) is what truly matters: does the generated SQL return the correct result when run against the real database? DB-GPT-Hub integrates the official test-suite-sql-eval framework, allowing you to validate models against both the standard Spider (95MB) and test-suite (1.27GB) database versions.
Recent results show fine-tuned CodeLlama-13B-Instruct achieving 74.6% EX on Spider—all via open weights and reproducible scripts.
Real-World Scenarios Where DB-GPT-Hub Delivers Value
Natural Language Interfaces for Internal Tools
Imagine your sales team needing to ask, “Which customers in EMEA had renewal rates above 80% last quarter?” without writing SQL. With DB-GPT-Hub, you can fine-tune a model on your company’s schema and query patterns, deploy it behind an API, and empower non-technical users with safe, accurate data access.
Domain-Specific SQL Assistants
Healthcare, finance, and logistics each have unique data structures and terminology. A general-purpose LLM won’t know that “admit_date” and “discharge_ts” belong to the “patient_encounters” table. But a model fine-tuned with DB-GPT-Hub on your internal dataset will.
Transparent, Vendor-Neutral Benchmarking
As an open platform, DB-GPT-Hub lets you compare tuning strategies (LoRA vs. QLoRA), model families (CodeLlama vs. Qwen), or data augmentations—without relying on opaque commercial APIs. This is critical for research labs, enterprise AI teams, and startups building defensible, auditable systems.
Getting Started in Under 10 Minutes
The workflow is intentionally simple:
- Install: Clone the repo and run
pip install -e .in thesrc/dbgpt_hub_sqldirectory. - Prepare Data: Drop the Spider dataset into
data/spider/and rungen_train_eval_data.sh. - Fine-Tune: Execute
train_sft.shwith your chosen model (e.g.,CodeLlama-7b-Instruct) and method (QLoRA by default). - Predict & Evaluate: Generate SQL with
predict_sft.shand score results using the built-in evaluator.
For rapid prototyping, pre-trained LoRA weights (e.g., CodeLlama-13B achieving 78.9% EX) are available on Hugging Face. You can even merge adapter weights into a full model for deployment using export_merge.sh.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
DB-GPT-Hub excels in fine-tuning scenarios but isn’t a plug-and-play chatbot. Key constraints to note:
- It assumes you have access to structured schema metadata (tables, columns, foreign keys), which must be included in the input prompt.
- While QLoRA reduces memory needs, training 13B models still requires ~13GB GPU RAM—manageable on a single A10 or 3090, but not on consumer laptops.
- Performance varies by query difficulty: “Easy” queries often exceed 90% accuracy, but “Extra Hard” cases (e.g., nested aggregations with filters) remain challenging even for tuned models.
Crucially, DB-GPT-Hub is not a prompting toolkit—if you’re only using in-context learning without tuning, other tools may suffice. But if you need reliable, domain-adapted SQL generation, fine-tuning is non-negotiable, and DB-GPT-Hub provides the most open, efficient path today.
Summary
DB-GPT-Hub fills a critical gap in the LLM-for-data ecosystem: it makes high-accuracy, fine-tuned Text-to-SQL accessible, reproducible, and production-ready. By standardizing data processing, tuning, and evaluation across leading open models—and enabling all of it on modest hardware—it empowers engineers, researchers, and product teams to move beyond fragile prompt hacks and build robust natural language database interfaces. Whether you’re benchmarking model performance or deploying an internal analytics assistant, DB-GPT-Hub gives you the open foundation to iterate fast and ship confidently.