Kimi-Dev is a state-of-the-art open-source large language model (LLM) purpose-built for software engineering tasks. Unlike generic coding assistants that generate syntactically plausible but unverified code, Kimi-Dev is trained to produce correct, test-passing patches in real repositories. It achieves 60.4% on SWE-bench Verified—the highest score among all open-source models in this rigorous benchmark—by leveraging a unique agentless training approach that simulates real-world developer workflows inside Docker environments. Every edit it proposes must pass the full test suite of the target repository to receive a reward, ensuring reliability beyond surface-level syntax.
This focus on verifiable correctness makes Kimi-Dev particularly valuable for teams and researchers who need automated solutions they can trust without extensive manual validation. Moreover, the model’s internal “skill priors”—learned through structured, single-turn reasoning—enable it to serve as a strong foundation for both workflow-based systems and more complex agent frameworks.
Why Kimi-Dev Delivers Practical Value
Built for Real Repositories, Not Just Code Snippets
Many AI coding tools excel at generating isolated functions but stumble when faced with large, real-world codebases. Kimi-Dev is different: it’s trained on the full context of GitHub repositories, complete with issue descriptions, file hierarchies, and existing test suites. During training, the model autonomously edits code inside Docker containers and only receives positive feedback when all tests pass. This aligns its behavior with professional software development standards, not just academic benchmarks.
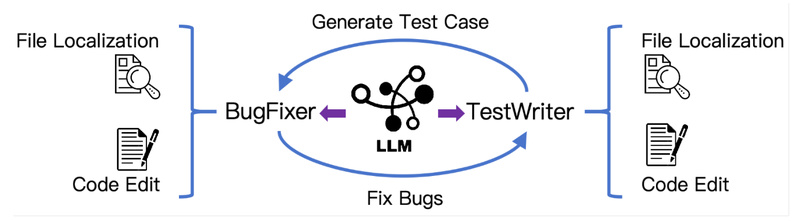
Bridges Agentless and Agentic Paradigms
Kimi-Dev demonstrates that agentless (single-turn, workflow-based) and agentic (multi-turn, interactive) approaches aren’t mutually exclusive. Through reinforcement learning, it learns core skills—file localization, precise code editing, and self-reflection—as reusable “priors.” When fine-tuned on just 5,000 public agent trajectories, Kimi-Dev powers SWE-agents to 48.6% pass@1 on SWE-bench, matching the performance of Claude 3.5 Sonnet (241022). This shows that structured, verifiable training can bootstrap intelligent agent behavior without requiring complex orchestration from day one.
Ideal Use Cases
Kimi-Dev shines in scenarios where correctness and integration into existing codebases matter more than conversational fluency:
- Automated bug fixing: Given an issue report and a codebase, Kimi-Dev identifies relevant files and generates patches that pass the project’s test suite.
- Unit test generation: It can write high-quality test cases that align with the project’s testing conventions and coverage goals.
- Repository-wide maintenance: Engineering teams can use it to triage and resolve technical debt or compatibility issues across large codebases with minimal human oversight.
These capabilities are especially useful for open-source maintainers, DevOps automation pipelines, and AI research labs developing next-generation software engineering agents.
How It Works: A Simple Two-Stage Workflow
Despite its advanced training, Kimi-Dev uses a straightforward inference pipeline that’s easy to integrate:
- File Localization: The model analyzes the issue description and repository structure to pinpoint which files are likely involved in the fix or test. This avoids the noise of processing the entire codebase.
- Code Editing: Once key files are identified, Kimi-Dev performs precise, context-aware edits—including bug corrections or test insertions—using the full content of those files as context.
This two-stage design balances efficiency with accuracy. Notably, unlike multi-step localization approaches that narrow down to line numbers early, Kimi-Dev passes the entire file to the editing stage, allowing deeper reasoning about dependencies and side effects.
The project provides ready-to-run scripts for both bug fixing and test writing, along with preprocessed repository structures to simplify setup.
Practical Considerations Before Adoption
While Kimi-Dev offers impressive capabilities, it comes with real-world constraints:
- Hardware requirements: The flagship Kimi-Dev-72B model requires significant GPU resources. The recommended inference setup uses 8 GPUs via vLLM with high memory utilization (e.g.,
--gpu-memory-utilization 0.95). - Task scope: It performs best on SWE-bench–style tasks—primarily Python repositories with comprehensive test suites. Performance may vary on languages or projects without robust testing infrastructure.
- Not a general-purpose chatbot: Kimi-Dev is optimized for verifiable code edits, not open-ended conversation or documentation generation. Use it as a specialized tool in your software engineering pipeline, not a replacement for general coding assistants.
That said, its open-source nature (available on Hugging Face and GitHub) and clear rollout examples make it accessible for experimentation, even if full deployment requires substantial compute.
Summary
Kimi-Dev redefines what’s possible with open-source coding LLMs by prioritizing test-verified correctness over superficial code generation. With its agentless training strategy, it learns transferable software engineering skills that benefit both standalone workflows and agent-based systems. For teams seeking reliable, automated solutions for bug fixing and test writing in real codebases, Kimi-Dev offers a powerful, production-aligned foundation—backed by top-tier benchmark results and open accessibility.