If you’re building computer vision systems that demand both high accuracy and real-world efficiency—without getting bogged down in architectural complexity—MambaVision is worth your attention. Developed by NVIDIA Research, MambaVision is a hybrid vision backbone that fuses the long-range modeling power of Vision Transformers (ViTs) with the computational efficiency of Mamba-style state-space models. The result? A model family that delivers state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on ImageNet-1K in both Top-1 accuracy and throughput, while natively supporting downstream tasks like object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation.
Unlike purely attention-based or purely recurrent architectures, MambaVision strikes a pragmatic balance: it uses Mamba blocks for efficient local and mid-range feature processing in early and middle stages, then introduces self-attention in later layers to capture critical long-range spatial dependencies. This design isn’t just theoretically elegant—it translates into measurable gains across benchmarks and flexible deployment options for practitioners.
Why MambaVision Stands Out
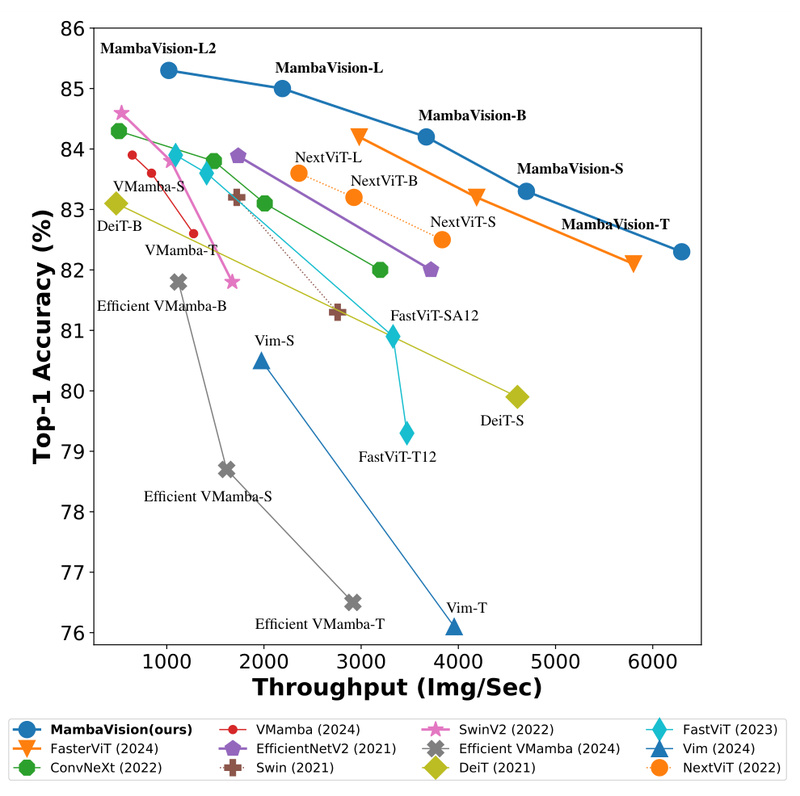
SOTA Accuracy and Throughput on ImageNet-1K
MambaVision redefines what’s possible in the accuracy-throughput trade-off. For example, MambaVision-T achieves 82.3% Top-1 accuracy with a throughput of 6,298 images/second on standard 224×224 inputs—outperforming many contemporary vision backbones in both metrics simultaneously. Larger variants like MambaVision-L3-512-21K push Top-1 accuracy to 88.1% on ImageNet-21K, demonstrating scalability without sacrificing inference speed relative to model size.
This dual optimization matters: in production environments, you often can’t afford to choose between “accurate but slow” and “fast but inaccurate.” MambaVision offers a Pareto-optimal alternative that excels at both.
Arbitrary Input Resolution Support
One of MambaVision’s most practical features is its native support for any input resolution—no architectural tweaks or retraining required. Whether you’re processing 224×224 thumbnails or high-resolution 512×512 medical or satellite images, the same model adapts seamlessly. This eliminates a common pain point in vision pipelines where resolution mismatches force costly preprocessing or custom model variants.
Hierarchical Multi-Scale Features for Downstream Tasks
MambaVision outputs features from four hierarchical stages, each at progressively reduced spatial resolution and increased channel depth (e.g., stage 1: 80 channels at 56×56; stage 4: 640 channels at 7×7). These multi-scale representations are ideal for dense prediction tasks.
Indeed, when paired with standard frameworks like Cascade Mask R-CNN or UPerNet, MambaVision backbones consistently outperform similarly sized ViTs and CNNs:
- Object detection: MambaVision-B achieves 52.8 box mAP on COCO.
- Semantic segmentation: MambaVision-L3-512-21K reaches 53.2 mIoU on ADE20K.
This makes MambaVision not just a classifier, but a full-featured vision backbone ready for real-world applications.
Ideal Use Cases for Engineers and Applied Researchers
MambaVision is particularly well-suited for scenarios where you need:
- High-throughput image classification at scale (e.g., content moderation, e-commerce tagging).
- Robust feature extraction for transfer learning or retrieval systems.
- End-to-end vision pipelines that require consistent performance from classification through to dense prediction (detection, segmentation).
- Flexible resolution handling, such as in video analysis or multi-sensor fusion where input sizes vary.
Its hybrid architecture reduces the quadratic complexity of pure Transformers while preserving their representational strength—ideal for teams seeking ViT-level performance without ViT-level compute costs.
Getting Started Is Simpler Than You Think
Despite its advanced design, integrating MambaVision requires minimal setup:
Option 1: Hugging Face (Recommended for Quick Prototyping)
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("nvidia/MambaVision-T-1K", trust_remote_code=True
)
You can run inference or extract multi-stage features with just a few lines—no custom ops or complex dependencies.
Option 2: Official pip Package
pip install mambavision
from mambavision import create_model
model = create_model('mamba_vision_T', pretrained=True)
Both approaches support any input resolution and integrate smoothly into standard PyTorch workflows. NVIDIA also provides Google Colab demos and validation scripts, so you can evaluate performance on your own data within minutes.
Important Considerations Before Adoption
While MambaVision offers compelling advantages, be mindful of these constraints:
- Licensing: Pretrained models are released under CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0, meaning they’re not cleared for commercial use without separate licensing from NVIDIA. Academic and research use is fully supported.
- Hardware Requirements: Larger models (e.g., L3 variants with 739M parameters) require substantial GPU memory—plan accordingly for deployment.
- Throughput Variability: Reported throughput and FLOPs are hardware-dependent. Always benchmark on your target infrastructure.
These aren’t blockers, but practical factors to weigh during technical evaluation.
Summary
MambaVision delivers a rare combination: SOTA accuracy, high throughput, resolution flexibility, and plug-and-play support for both classification and dense vision tasks. For project leads, ML engineers, and applied researchers evaluating next-generation vision backbones, it presents a compelling alternative to pure Transformers or CNNs—especially when efficiency and scalability are non-negotiable. With easy integration via Hugging Face or pip, and strong results across ImageNet, COCO, and ADE20K, MambaVision is ready to accelerate your vision pipeline today—provided your use case aligns with its non-commercial license terms.