Evaluating how well large language models (LLMs) retrieve critical facts and perform reasoning over long documents remains a major challenge for technical decision-makers. Traditional evaluation approaches either rely on real-world texts—where a model’s pre-existing knowledge can mask true retrieval performance—or pad contexts with irrelevant filler to reach target lengths, muddying the signal.
NeedleBench, introduced by the OpenCompass team, directly addresses these limitations by offering a synthetic, controllable, and bilingual benchmark designed specifically to stress-test LLMs on two essential capabilities: information retrieval and reasoning under varying information densities. Built into the OpenCompass evaluation platform, NeedleBench enables engineers, researchers, and product leads to make data-driven decisions about which models truly excel in long-context applications—beyond marketing claims or generic leaderboard scores.
Why Existing Long-Context Benchmarks Fall Short
Most long-context evaluations suffer from two fundamental flaws:
- Knowledge contamination: When models are tested on real-world articles or books, their responses may stem from memorized knowledge rather than actual in-context retrieval.
- Artificial context inflation: Many benchmarks insert meaningless filler text (e.g., repeated phrases or random paragraphs) to extend context length, which doesn’t reflect realistic information distribution and reduces evaluation fidelity.
These issues obscure whether a model is genuinely retrieving and reasoning over provided information—or simply regurgitating internal knowledge. As a result, teams risk selecting models that underperform in production scenarios involving legal contracts, scientific literature, or customer support logs where precise in-context understanding is non-negotiable.
How NeedleBench Solves the Problem
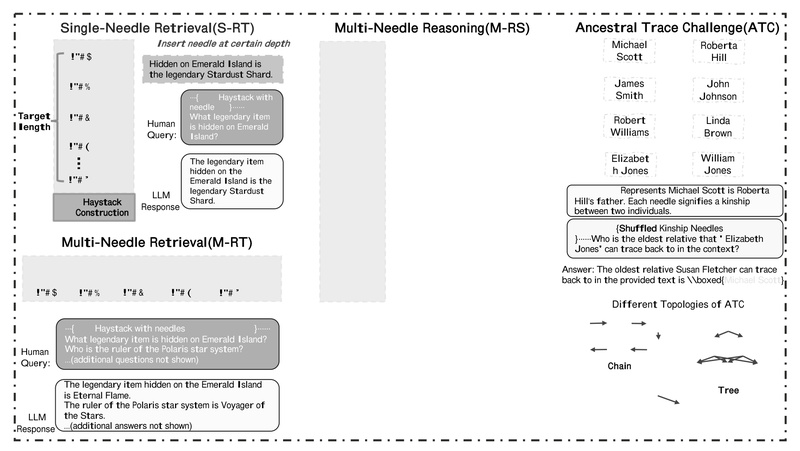
NeedleBench introduces a principled, synthetic framework that embeds key data points—”needles”—at varying depths within a controlled context. This design eliminates confounding factors and isolates the model’s ability to locate and use relevant information.
Two Distinct Evaluation Scenarios
NeedleBench defines two canonical task types to capture different real-world demands:
- Information-sparse tasks: A single, critical fact (the “needle”) is buried within a large body of irrelevant text. This simulates simple retrieval challenges, such as finding a clause in a 50-page contract.
- Information-dense tasks (Ancestral Trace Challenge): Relevant facts are continuously distributed throughout the context, requiring the model to track, integrate, and reason over multiple pieces of information—mirroring complex scenarios like tracing genealogical relationships or reconstructing scientific arguments across a research paper.
Adaptive Context Lengths and Bilingual Support
Context lengths in NeedleBench dynamically scale with task complexity, ensuring evaluations remain meaningful across difficulty levels. Additionally, all tasks are available in both English and Chinese, making it uniquely suited for global teams or multilingual applications.
This synthetic yet realistic design provides actionable insights: for instance, recent high-performing reasoning models like Deepseek-R1 and OpenAI’s o3 may dominate math benchmarks but exhibit significant failure in dense-reasoning tasks—even at relatively short context lengths. NeedleBench also exposes subtle failure modes like “under-thinking”, where models prematurely conclude reasoning despite ample contextual evidence.
Ideal Use Cases for Technical Teams
NeedleBench is particularly valuable in the following scenarios:
- Selecting LLMs for long-document question answering, such as in legal tech or enterprise knowledge bases.
- Validating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines under controlled information densities to ensure robustness.
- Benchmarking models for scientific or technical summarization, where missing a single detail can alter conclusions.
- Informing product design decisions by quantifying whether a model can support multi-hop reasoning in customer support or diagnostic systems.
By revealing gaps between a model’s general reasoning prowess and its long-context capabilities, NeedleBench helps avoid costly mismatches between model performance and product requirements.
Getting Started with NeedleBench
NeedleBench is integrated into the OpenCompass evaluation platform, which is open-source and widely adopted. Running evaluations is straightforward:
-
Install OpenCompass via pip or from source:
pip install -U opencompass # Or for full dataset support: pip install "opencompass[full]"
-
Prepare datasets: OpenCompass can automatically download required data or stream it on-demand via ModelScope, avoiding large local storage requirements.
-
Run a NeedleBench evaluation using either CLI or Python scripts:
opencompass --models hf_internlm2_5_1_8b_chat --datasets needlebench_en_sparse_gen
The platform supports Hugging Face, vLLM, and LMDeploy backends for accelerated inference, and works seamlessly with both open-source and API-based models (including OpenAI’s o1 series). No specialized infrastructure is needed—just a standard Python environment and GPU access.
Key Limitations to Consider
While NeedleBench offers rigorous control, it is a synthetic benchmark. Its results should complement—not replace—domain-specific testing on real documents. Additionally, interpreting performance requires understanding the distinction between sparse retrieval and dense reasoning; a model strong in one may falter in the other.
Finally, users must engage with the OpenCompass framework, which, while well-documented, introduces a modest learning curve for those new to programmatic evaluation workflows.
Summary
NeedleBench fills a critical gap in the LLM evaluation ecosystem by providing a clean, controllable, and insightful method to assess how models handle long-context retrieval and reasoning. For technical decision-makers, it offers a reliable way to cut through hype and identify models that truly perform under realistic information-density conditions. By integrating NeedleBench early in the model selection pipeline, teams can build more robust, trustworthy, and effective AI applications—grounded in evidence, not assumptions.