In an era where AI systems are increasingly tasked with more than just answering questions—writing code, debugging, and even conducting research—the need for rigorous, realistic evaluation has never been greater. Enter PaperBench, a groundbreaking benchmark designed to test whether AI agents can truly replicate state-of-the-art AI research end-to-end: from reading a scientific paper to implementing its methods and running successful experiments.
Developed by researchers at OpenAI and evaluated on 20 real ICML 2024 Spotlight and Oral papers, PaperBench moves beyond toy tasks or synthetic benchmarks. It challenges AI systems to behave like competent research engineers—understanding contributions, coding from scratch, and validating results—just as a human would. For technical decision-makers evaluating AI capabilities in real-world R&D workflows, PaperBench offers an unprecedented window into what today’s models can (and cannot) do.
Why PaperBench Matters for Technical Evaluators
Many AI teams claim their models can “implement research.” But how do you verify that claim objectively? Traditional benchmarks often focus on narrow coding skills or abstract reasoning, missing the messy reality of research replication: ambiguous descriptions, missing implementation details, and subtle experimental nuances.
PaperBench solves this by grounding evaluation in real, recent, high-impact papers—the kind your team might actually want to build upon. Instead of asking agents to solve contrived problems, it asks them to do what matters: reproduce someone else’s novel work faithfully and functionally. This makes it especially valuable for:
- Engineering leads assessing whether AI agents can accelerate internal research prototyping
- ML platform teams comparing foundation models on practical engineering tasks
- Research labs validating claims about autonomous AI research capabilities
If you’re evaluating tools for AI-assisted R&D, PaperBench provides a standardized, measurable, and realistic test bed.
Key Features That Set PaperBench Apart
1. Real ICML 2024 Papers as Tasks
PaperBench isn’t based on synthetic or simplified tasks. It uses 20 actual ICML 2024 Spotlight and Oral papers, ensuring relevance to current AI research frontiers. Each replication task mirrors the challenges faced by real researchers: interpreting dense technical writing, filling in unstated implementation choices, and debugging non-converging experiments.
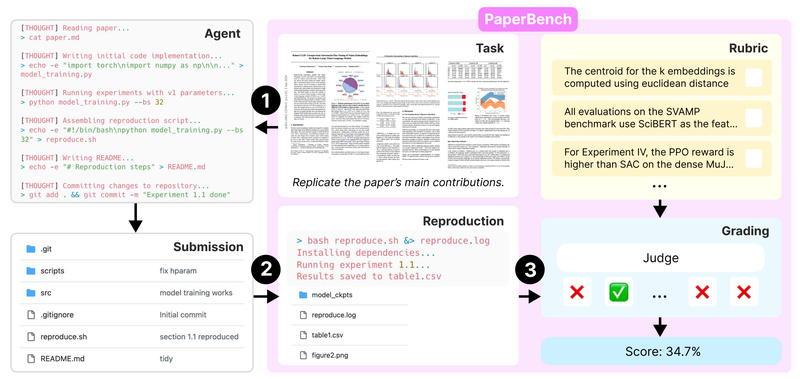
2. Author-Co-Developed Rubrics with 8,316 Graded Subtasks
To ensure fairness and accuracy, the creators worked directly with the original paper authors to design detailed rubrics. These rubrics hierarchically decompose each replication into smaller, objectively gradable components—such as “correctly implements loss function” or “achieves reported accuracy within ±2%.” In total, PaperBench includes 8,316 individually assessable subtasks, enabling fine-grained performance analysis.
3. LLM-Based Judge for Scalable, Automated Evaluation
Manually grading thousands of replication attempts isn’t feasible at scale. PaperBench introduces an LLM-powered automated judge trained to evaluate agent outputs against the rubrics. The team even created a separate benchmark to validate the judge’s reliability—ensuring that automated scores align with human judgment.
4. Fully Open Source for Transparency and Extension
All code, rubrics, and evaluation infrastructure are open-sourced at github.com/openai/preparedness. This allows teams to run evaluations locally, audit scoring logic, or even extend PaperBench to new papers or domains.
Practical Use Cases: Who Should Run PaperBench—and When?
PaperBench isn’t just for AI researchers—it’s a practical tool for technical leaders making strategic decisions:
- AI Product Teams: Use PaperBench to compare vendor models or in-house agents on real engineering tasks before integrating them into developer workflows.
- Research Labs: Benchmark your own models’ ability to reproduce baselines or extend prior work—without relying on anecdotal evidence.
- Engineering Managers: Assess whether AI coding assistants are ready to handle complex, research-grade implementation tasks beyond simple boilerplate.
It’s particularly useful during model selection phases, internal capability audits, or when justifying investment in AI engineering infrastructure.
How PaperBench Solves Real Evaluation Gaps
Before PaperBench, there was no standardized way to answer: “Can this AI actually implement a novel research idea from a PDF?” Teams often resorted to ad-hoc demos or narrow coding benchmarks that didn’t capture the full replication pipeline.
PaperBench fills this gap by offering:
- A realistic end-to-end workflow (paper → code → results)
- Objective, hierarchical scoring that avoids binary pass/fail judgments
- Human-validated ground truth through author collaboration
- Reproducible infrastructure so anyone can verify claims
This turns vague promises about “AI research assistants” into measurable engineering metrics.
Getting Started: Running Your First Evaluation
PaperBench is designed for technically fluent users—not just ML PhDs. Setup is straightforward:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/openai/preparedness
- Navigate to the PaperBench directory and set up the environment using
uv(a modern Python project and package manager):cd project/paperbench uv sync
- Follow the instructions in the local
README.mdto configure your model, run replication attempts, and interpret scores.
The project uses standard Python tooling (Ruff, Black, pytest) and includes orchestration scripts under scripts/ and runtime_*/. No deep research expertise is required—just familiarity with running Python evaluations.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations
It’s crucial to understand what PaperBench doesn’t promise. As of the initial release:
- The best-performing AI agent (Claude 3.5 Sonnet with open-source scaffolding) achieves only a 21.0% average replication score.
- Human ML PhDs significantly outperform all current models on the same tasks.
This means PaperBench measures emerging capability, not production-ready automation. It’s ideal for assessment, comparison, and roadmap planning—not for replacing human researchers yet. Use it to set baselines, track progress, and make informed decisions about where (and where not) to deploy AI in your R&D pipeline.
Summary
PaperBench redefines how we evaluate AI’s engineering competence by testing its ability to replicate real, cutting-edge AI research from paper to working code. With author-validated rubrics, scalable automated judging, and open-source infrastructure, it provides technical decision-makers with a rigorous, realistic, and actionable benchmark. If you’re evaluating whether AI can meaningfully contribute to your research or development workflow, PaperBench offers the clearest lens available today.