Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) has become essential for extracting fine-grained opinions from text—such as determining whether a customer loves a laptop’s battery life but dislikes its keyboard. However, reproducing state-of-the-art ABSA results often demands deep NLP expertise, fragmented codebases, and significant engineering effort.
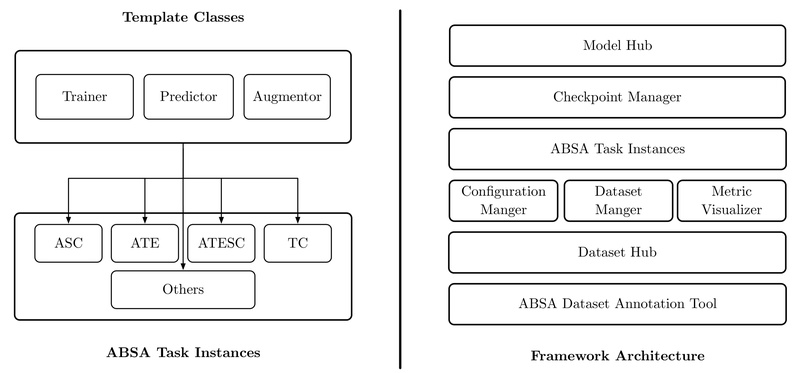
PyABSA directly addresses these pain points. Released as a modular, reproducible framework built on PyTorch, it enables anyone—from software engineers to product analysts—to run, train, and evaluate ABSA models with just a few lines of code. Whether you’re analyzing restaurant reviews, monitoring social media, or prototyping in academic research, PyABSA eliminates the usual barriers to entry by unifying 29 models, 26 datasets, and multiple ABSA subtasks under one consistent API.
Originally introduced in a CIKM 2023 paper, PyABSA was designed specifically to lower the reproducibility barrier in ABSA. It’s not just a research toolkit—it’s production-ready, supports multilingual inference out of the box, and includes practical features like data augmentation and human-in-the-loop annotation helpers to tackle data scarcity.
Key Features That Save Time and Reduce Complexity
Unified API Across ABSA Subtasks
PyABSA treats ABSA not as a single problem but as a family of related tasks—and provides a clean, consistent interface for each:
- APC (Aspect Polarity Classification): Predict sentiment (positive/negative/neutral) for a given aspect.
- ATEPC (Aspect Term Extraction & Polarity Classification): Extract aspect terms and classify their sentiment in one pass.
- ASTE (Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction): Identify full (aspect, opinion, sentiment) triplets.
- ASQP/ACOS: Extract quadruples like (aspect, category, opinion, sentiment).
Despite these differences, using any task follows the same pattern: import a module, load a checkpoint, and call .predict(). This consistency drastically reduces cognitive load and code duplication.
Built-In Model Zoo with Automatic Checkpoint Management
PyABSA integrates 29 pre-trained models, ranging from BERT-based architectures to lightweight alternatives. The framework automatically handles checkpoint discovery and downloading via its available_checkpoints() utility. No more hunting for model weights or wrestling with version mismatches—PyABSA resolves local and remote checkpoints seamlessly.
One-Line Inference, Zero Configuration
You don’t need to manage tokenizers, data loaders, or device placement. PyABSA auto-selects CPU or GPU, handles input preprocessing, and returns structured results. For example:
from pyabsa import AspectTermExtraction as ATEPC
extractor = ATEPC.AspectExtractor('multilingual', auto_device=True)
result = extractor.predict(['The service was amazing, but the food was cold.'])
This returns detected aspects (“service”, “food”), their associated opinions (“amazing”, “cold”), and predicted polarities—all without writing a single line of data pipeline code.
Tools for Real-World Data Challenges
Beyond inference, PyABSA includes text augmentation techniques to combat limited labeled data and annotation helpers to accelerate dataset creation. These features are especially valuable when working with domain-specific feedback (e.g., healthcare or finance) where public datasets fall short.
Real-World Use Cases Where PyABSA Shines
Product & Service Feedback Analysis
E-commerce platforms and SaaS companies can use PyABSA to automatically parse customer reviews into actionable insights. Instead of coarse “4-star” ratings, they gain structured feedback like: “Users love the app’s UI (positive) but complain about slow loading times (negative).”
Social Media & Brand Monitoring
Marketing teams can monitor brand mentions across Twitter, Reddit, or forums, identifying which product features trigger positive or negative sentiment—enabling faster response and product iteration.
Academic and Industrial Prototyping
Researchers evaluating new ABSA methods can use PyABSA as a reproducible baseline. Engineers building sentiment-aware features in applications (e.g., chatbots, recommendation systems) can integrate PyABSA directly without developing models from scratch.
Critically, PyABSA requires no PhD in NLP. Its design assumes the user is competent in Python but not necessarily in transformer architectures or custom loss functions.
How to Get Started in Minutes
Getting PyABSA running is intentionally frictionless:
-
Install via PyPI:
pip install -U pyabsa
-
Run your first inference (as shown above): load a multilingual model and analyze a sentence.
-
Scale to datasets using built-in enums:
from pyabsa import AspectPolarityClassification as APC classifier = APC.SentimentClassifier('multilingual') result = classifier.batch_predict(target_file=APC.APCDatasetList.Laptop14)
The framework includes ready-to-use datasets like Laptop14 and Restaurant16, so you can validate performance immediately. For custom data, PyABSA provides clear formatting guidelines and semi-automatic annotation scripts.
Documentation is hosted at pyabsa.readthedocs.io (though per instructions, we omit live links here), and examples are included in the examples-v2/ directory of the GitHub repo.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
PyABSA is powerful but not magic. Users should be aware of a few constraints:
- Breaking changes in v2: Scripts written for earlier versions may require updates.
- Initial download latency: The first use of a model triggers an automatic download—plan for this in production deployment.
- GPU recommended but optional: Training and large-batch inference benefit from GPU acceleration, but CPU-only usage is fully supported for inference.
- Advanced features need extra deps: Visualization and certain augmentation methods require optional dependencies—these are clearly documented and not installed by default to keep the core lightweight.
These are reasonable trade-offs for a framework that prioritizes accessibility without sacrificing rigor.
Why PyABSA Stands Out Among ABSA Tools
Many open-source ABSA projects offer isolated model implementations with inconsistent interfaces, missing evaluation scripts, or no pre-trained weights. PyABSA solves this fragmentation by providing:
- End-to-end reproducibility: From training to inference to metric visualization.
- Community-driven dataset hub (ABSADatasets): Ensures data availability and standardization.
- Modular design: New models or tasks can be plugged in without rewriting core logic.
- Focus on practitioner needs: Features like perplexity calculation, error tolerance (
ignore_error=True), and result saving simplify real-world usage.
In short, PyABSA isn’t just another research code dump—it’s a thoughtfully engineered framework built for both experimentation and deployment.
Summary
PyABSA lowers the barrier to high-quality Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis by combining modularity, reproducibility, and ease of use. With support for multiple subtasks, automatic model management, and practical tooling for data-scarce scenarios, it empowers technical teams to extract nuanced sentiment insights without deep NLP expertise. Whether you’re a developer building a review analytics dashboard or a researcher benchmarking new methods, PyABSA offers a streamlined, production-ready path from idea to implementation.