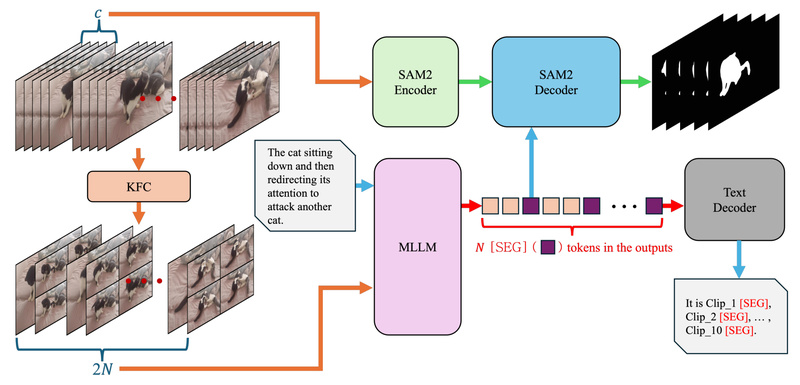
Sa2VA represents a significant leap forward in multimodal AI by seamlessly integrating the strengths of SAM2—Meta’s state-of-the-art video object segmentation foundation model—with LLaVA, a leading vision-language model. The result is a unified architecture capable of interpreting natural language instructions and precisely segmenting, tracking, and reasoning about objects in both static images and dynamic video sequences. Unlike traditional pipelines that require separate models for vision understanding, language parsing, and segmentation, Sa2VA collapses these stages into a single, end-to-end system that responds to prompts like “segment the girl wearing the yellow dress” with pixel-accurate masks across all relevant video frames.
This capability earned Sa2VA’s enhanced variant, SaSaSa2VA, first place in the RVOS (Referring Video Object Segmentation) track of the 7th LSVOS Challenge at ICCV 2025, outperforming the runner-up by a substantial 2.80 points in J&F score—a widely accepted metric for video segmentation quality. Crucially, Sa2VA is not just a competition-winning prototype; it’s a fully open-sourced, production-ready toolkit with pre-trained models, inference scripts, evaluation benchmarks, and interactive demos, making it immediately accessible to practitioners across industries.
Core Capabilities and Technical Strengths
Unified Image and Video Understanding in One Model
Sa2VA is the first open model to support dense grounded understanding across both images and videos within a shared architecture. Whether your input is a single photograph or a multi-frame video clip, the same model processes it without requiring modality-specific adaptations. This eliminates the need to maintain separate pipelines for image captioning, video QA, or object tracking—reducing engineering complexity and deployment overhead.
Natural Language–Guided Segmentation and Tracking
At its heart, Sa2VA enables referring segmentation: given a phrase like “the man holding a red umbrella,” it identifies and segments that specific entity consistently across time in a video. This goes beyond detection—it produces high-fidelity masks that reflect object shape, occlusion, and motion, grounded directly in linguistic descriptions. This is particularly valuable in scenarios where object identity is defined contextually rather than by category (e.g., “the dog that barked first”).
Minimal Instruction Tuning, Maximum Flexibility
Sa2VA achieves strong performance with only lightweight instruction tuning, meaning it generalizes well to novel prompts without extensive retraining. Users can issue diverse instructions—from segmentation requests (“segment the cyclist”) to open-ended questions (“What is the mood of this scene?”)—and receive coherent, grounded responses. This makes the model highly adaptable for rapid prototyping and iterative development.
Scalable Model Sizes for Diverse Hardware Constraints
The project offers a comprehensive model zoo ranging from Sa2VA-1B (suitable for single-GPU setups) to Sa2VA-26B (for high-accuracy enterprise applications). Models are built on leading vision-language backbones, including InternVL2.5, InternVL3, Qwen2.5-VL, and Qwen3-VL, allowing users to trade off between latency, memory footprint, and performance based on their use case.
Practical Applications for Technical Teams
Sa2VA directly addresses real-world challenges that previously required stitching together multiple specialized systems:
- Video Editing & Content Creation: Automatically isolate subjects based on spoken or typed descriptions (e.g., “blur the background behind the speaker”), enabling non-destructive, language-driven editing workflows.
- Surveillance & Content Moderation: Flag or redact specific actions or individuals in video feeds using natural language rules (“track any person entering the restricted zone”), improving auditability and compliance.
- Accessibility Tools: Generate dynamic scene descriptions for visually impaired users by grounding language in visual content (“a woman in a blue coat is walking toward the bus stop”).
- Multimodal AI Research: Serve as a foundation for exploring grounded reasoning, video QA, or instruction-following in dynamic scenes, with support for fine-tuning on custom datasets.
Getting Started: From Demo to Deployment
Sa2VA lowers the barrier to entry through multiple access points:
-
Try without setup: Use public Gradio demos (hosted by both the authors and Hugging Face) or run inference via Replicate to test the model interactively.
-
Local inference in minutes: With just a folder of video frames and a single command, users can generate segmentation masks or answers:
python demo/demo.py /path/to/video_frames --model_path ByteDance/Sa2VA-8B --text "Please segment the person wearing sunglasses."
Outputs—including masks, visual overlays, and text responses—are saved automatically to a specified directory.
-
Fine-tuning support: For domain-specific tasks, Sa2VA provides example configurations and data loaders to adapt the model to custom referring segmentation datasets, such as variants of RefCOCO or proprietary video annotations.
Limitations and Operational Considerations
While powerful, Sa2VA has practical constraints that teams should evaluate:
- Hardware requirements: Larger models (8B and above) perform best on systems with multiple high-memory GPUs (e.g., A100s), and may be impractical for edge deployment without quantization or distillation.
- Input quality dependency: Performance assumes reasonably clear, well-sampled video frames; extremely low-frame-rate or highly compressed videos may degrade segmentation accuracy.
- Prompt sensitivity: Like all language-conditioned systems, Sa2VA performs best with concrete, visually grounded descriptions. Abstract or ambiguous prompts (“segment the important object”) may yield inconsistent results.
- Fine-tuning complexity: Custom training requires familiarity with multimodal data formatting and distributed training setups, though starter examples are provided.
Summary
Sa2VA solves a critical pain point in applied computer vision: the fragmentation of language understanding and pixel-level object manipulation. By unifying SAM2’s segmentation prowess with LLaVA’s linguistic reasoning in a single, open, and scalable framework, it enables engineers and researchers to build applications that truly understand what users mean—and show it with precise visual grounding. Its top-tier performance in the ICCV 2025 LSVOS Challenge validates its robustness, while its modular design and open-source release make it a practical choice for teams looking to integrate language-guided video understanding into real products, research projects, or internal tools—without reinventing the wheel.