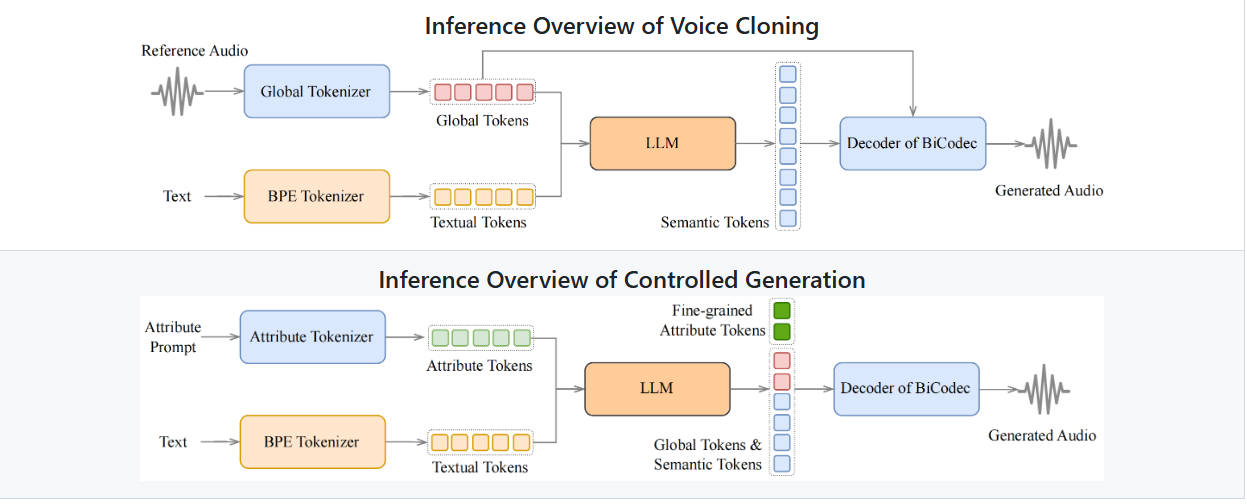
Overview
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI-powered speech synthesis, complexity has long been the price of quality. Traditional text-to-speech (TTS) systems often rely on multi-stage pipelines—separate modules for linguistic modeling, prosody prediction, acoustic feature generation, and waveform synthesis—making them difficult to deploy, customize, or scale. Enter Spark-TTS, a breakthrough system that reimagines TTS through the lens of large language models (LLMs). Built on Qwen2.5, Spark-TTS eliminates auxiliary components like vocoders or flow-matching modules by directly generating speech from a single-stream, decoupled token representation. The result? High-fidelity, zero-shot voice cloning and fine-grained speaker control—all within a streamlined, single-model architecture.
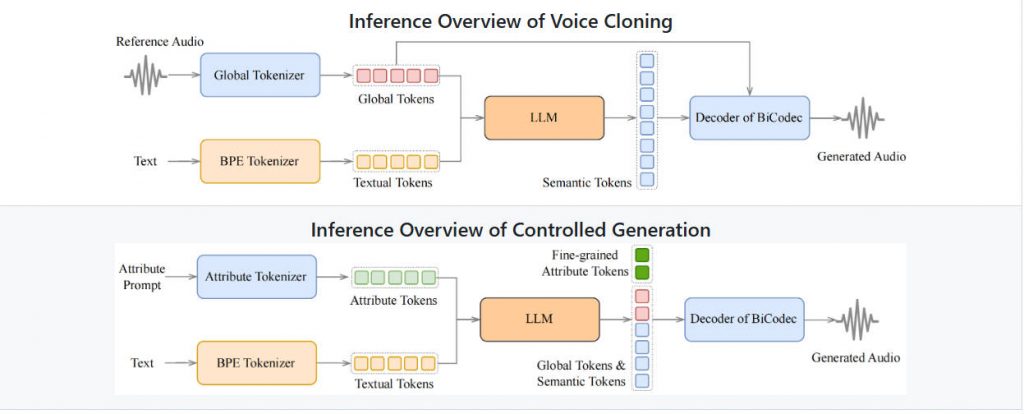
Why Spark-TTS Stands Out
A Simpler, Yet More Powerful Architecture
Unlike conventional LLM-based TTS systems that predict multiple codebooks or require post-processing with diffusion or flow-based models, Spark-TTS uses BiCodec, a novel speech codec that splits speech into two complementary token streams:
- Semantic tokens: Low-bitrate representations capturing linguistic content.
- Global tokens: Fixed-length vectors encoding speaker attributes like gender, pitch, and speaking style.
This disentanglement enables Spark-TTS to leverage the reasoning power of Qwen2.5 via a chain-of-thought (CoT) generation strategy, allowing the model to first infer high-level speaker traits and then synthesize speech accordingly—all in one forward pass. No extra models. No complex decoding. Just clean, efficient inference.
Zero-Shot Voice Cloning—No Training Required
One of Spark-TTS’s most compelling features is its ability to clone a voice from just a few seconds of reference audio, even for speakers never seen during training. This zero-shot capability works robustly across English and Chinese, and handles code-switching (mixing languages within a sentence) with remarkable naturalness. For developers building multilingual applications or personalized assistants, this removes the bottleneck of collecting and fine-tuning on speaker-specific data.
Precise Control Over Voice Characteristics
Beyond cloning, Spark-TTS supports parameterized voice creation. You don’t need a reference audio at all—you can specify traits like:
- Gender (male/female/neutral)
- Pitch level
- Speaking rate
This makes it ideal for generating consistent virtual personas in games, educational tools, or customer service bots, where brand-aligned vocal identity matters more than mimicking a real person.
Real-World Applications
Spark-TTS shines in scenarios where speed, flexibility, and quality intersect:
- Personalized voice assistants that adapt to user preferences without retraining.
- Multilingual audiobook platforms that seamlessly blend languages while preserving speaker identity.
- Gaming and entertainment studios creating dynamic NPCs with custom voices on demand.
- Startups and researchers prototyping TTS features rapidly, thanks to the model’s plug-and-play design and publicly available pre-trained weights.
Getting Started Is Effortless
The project lowers the barrier to entry significantly:
- Install via Conda (
python=3.12) andpip install -r requirements.txt. - Download the pre-trained model (
SparkAudio/Spark-TTS-0.5B) from Hugging Face usinggit lfsorhuggingface_hub. - Run inference either through a simple CLI command or the included Web UI.
For voice cloning, provide a short prompt audio and its transcript. For voice creation, adjust sliders or parameters in the UI to define your desired speaker. A infer.sh script in the example/ directory lets you generate your first sample in seconds.
Moreover, Spark-TTS supports NVIDIA Triton Inference Serving with TensorRT-LLM, achieving a real-time factor (RTF) as low as 0.07 on an L20 GPU—making it production-ready for high-throughput applications.
Current Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While Spark-TTS delivers impressive out-of-the-box performance, two key resources remain unreleased (as noted in the project’s GitHub to-do list):
- The training code
- The VoxBox dataset (a 100,000-hour multilingual corpus with rich attribute annotations)
This means users can use and evaluate the model, but cannot retrain or fine-tune it—at least not yet. Additionally, official support is limited to English and Chinese; other languages may not work reliably.
Importantly, the authors emphasize responsible usage: Spark-TTS must not be used for impersonation, fraud, or deepfake creation. The license restricts deployment to academic, educational, or legitimate commercial applications that comply with local laws and ethical AI principles.
Summary
Spark-TTS represents a significant step toward simpler, smarter, and more controllable speech synthesis. By collapsing the TTS pipeline into a single LLM and decoupling speech into semantic and speaker tokens, it achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot cloning and fine-grained voice control—without sacrificing efficiency. For teams tired of maintaining brittle, multi-component TTS stacks, Spark-TTS offers a compelling alternative: deploy fast, customize easily, and scale confidently. If your project demands high-quality, flexible, and ethically sound voice generation, Spark-TTS is worth serious consideration.