Verl (short for Volcano Engine Reinforcement Learning) is an open-source, production-ready framework designed specifically for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) in large language models (LLMs). Developed by ByteDance’s Seed team and released as the official implementation of the HybridFlow paper, Verl tackles the core inefficiencies that plague traditional RLHF pipelines—especially when scaling to massive models and complex multi-phase workflows involving both training and generation.
Unlike conventional reinforcement learning systems that rely on rigid, single-controller execution models, Verl introduces a hybrid-controller architecture that decouples computation from communication. This design enables both flexibility in expressing diverse RL algorithms and high throughput during execution—delivering up to 20.57× speedups over existing baselines across a range of RLHF workloads.
Whether you’re fine-tuning a 32B reasoning model for math competitions or orchestrating RLHF on a 671B MoE architecture across hundreds of GPUs, Verl provides the infrastructure, modularity, and performance needed to make it feasible—and efficient.
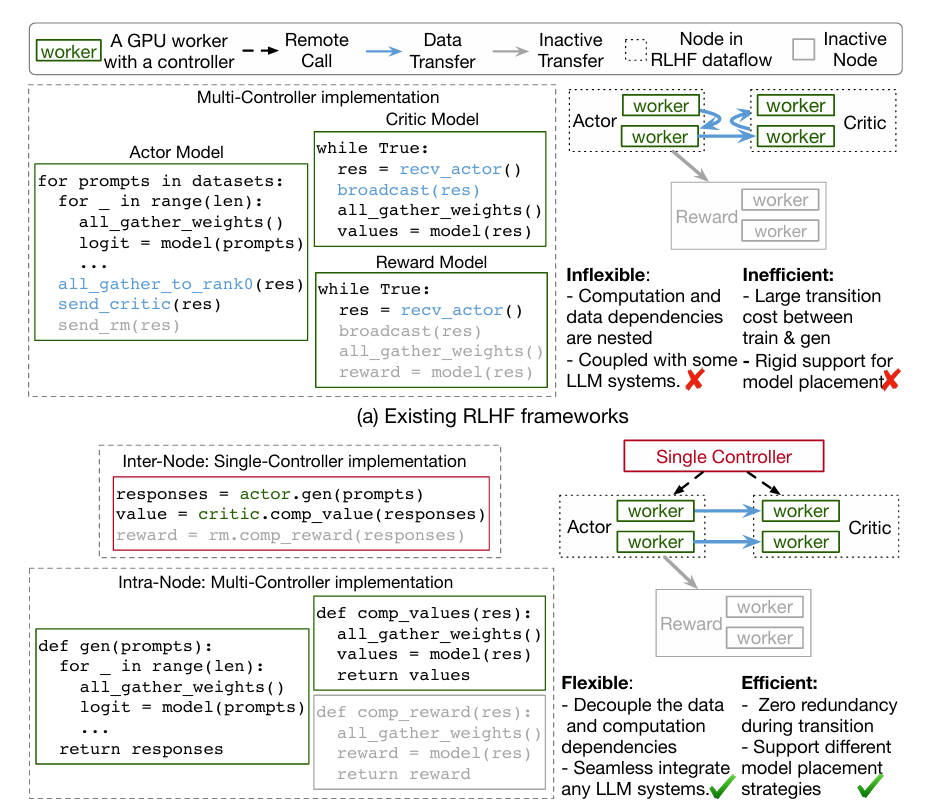
Why Traditional RLHF Frameworks Struggle
Standard RLHF pipelines involve a complex dataflow: actor models generate rollouts, reward models score them, and critic/policy networks update based on those rewards. In large-scale LLM settings, each “node” in this flow becomes a distributed training or inference job, and data dependencies turn into many-to-many communication patterns.
Legacy frameworks often use a single controller to manage both intra-node computation (e.g., forward/backward passes) and inter-node communication (e.g., transferring rollouts from actors to critics). This leads to high dispatch overhead, poor resource utilization, and inflexible algorithm expression—especially when switching between training and inference phases.
Alternative systems adopt multi-controller designs, but these often tightly couple communication logic with model parallelism, making it hard to integrate with existing LLM stacks like FSDP, vLLM, or Megatron-LM.
Verl’s Core Innovation: The HybridFlow Architecture
Verl solves these problems through HybridFlow, a novel programming model that blends the best of both worlds:
- Single-controller simplicity for high-level orchestration of the RL dataflow.
- Multi-controller efficiency for distributed intra-node execution.
This is achieved via a hierarchical API design that cleanly separates:
- Computation: What each model (actor, critic, reward) does.
- Data dependencies: How outputs from one component feed into another.
- Device mapping: Where each component runs (e.g., actor on inference-optimized GPUs, critic on training-optimized ones).
As a result, users can express complex algorithms like PPO, GRPO, or DAPO in just a few lines of code—while the system handles efficient scheduling, memory management, and communication under the hood.
Key Features That Deliver Real-World Value
1. Seamless Integration with Leading LLM Stacks
Verl works out of the box with:
- Training backends: FSDP, FSDP2, Megatron-LM (including expert parallelism for MoE models up to 671B parameters).
- Inference engines: vLLM (≥0.8.2), SGLang, and Hugging Face Transformers.
- Model hubs: Official support for Qwen-3, Qwen-2.5, Llama3.1, Gemma2, DeepSeek-LLM, and more.
This means teams already invested in these ecosystems can adopt Verl without rewriting their core infrastructure.
2. Algorithm Flexibility Without Performance Trade-offs
Verl supports a wide and growing list of RLHF algorithms:
- On-policy: PPO, GRPO, ReMax, RLOO, PRIME, KL_Cov
- Advanced variants: DAPO (SOTA on AIME 2024), VAPO, PF-PPO (ICML 2025), DrGRPO
- Emerging paradigms: Self-play (SPPO), multi-turn tool calling, vision-language RLHF (Qwen2.5-VL, Kimi-VL)
Each algorithm is implemented as a recipe—a reproducible, end-to-end training script that includes data loading, reward function definition, and hyperparameter tuning.
3. Efficient Actor Resharding with 3D-HybridEngine
One of RLHF’s biggest bottlenecks is switching an actor model between training mode (requiring optimizer states, gradients) and generation mode (requiring KV cache, high-throughput decoding). Traditional systems duplicate the model or incur heavy communication.
Verl’s 3D-HybridEngine eliminates memory redundancy and minimizes communication during this transition—enabling smooth, high-throughput alternating between rollouts and updates.
4. Scalability and Resource Efficiency
- Scales to hundreds of GPUs with expert and tensor parallelism.
- Supports multi-GPU LoRA for memory-efficient RL fine-tuning.
- Integrates FlashAttention-2, sequence packing, and sequence parallelism for faster training.
- Compatible with AMD ROCm (via FSDP + vLLM/SGLang), with Megatron support in progress.
Ideal Use Cases
Verl is particularly well-suited for:
- Reasoning-focused LLM alignment: Training models that excel at math (AIME), coding (Codeforces), or scientific QA (GPQA), as demonstrated by DAPO, VAPO, and Seed-Thinking-v1.5.
- Massive-scale RLHF: Running PPO or GRPO on models like DeepSeek-671B or Qwen3-235B using Megatron-LM backend.
- Agent training: Multi-turn interactions with tool calling, sandbox execution, or environment feedback—supported via verl-agent and related recipes.
- Vision-language alignment: Applying RLHF to VLMs using multimodal reward signals.
If your team uses Hugging Face models or Megatron-based training pipelines, Verl integrates with minimal friction.
Getting Started Is Straightforward
Verl emphasizes developer experience:
- Install via pip or from source.
- Run a full PPO or GRPO pipeline in minutes using provided recipes.
- Track experiments with Weights & Biases, TensorBoard, MLflow, or SwanLab.
- Extend the framework by implementing new reward functions, adding custom models, or plugging in new backends.
Documentation includes step-by-step guides for:
- Preparing post-training data
- Writing verifiable reward functions (e.g., for code execution or math proof checking)
- Configuring FSDP2 for optimal memory and throughput
- Deploying actor and critic on separate GPU pools
Limitations and Practical Notes
While Verl is highly capable, users should be aware of a few current constraints:
- vLLM version requirement: Must use vLLM ≥ 0.8.2; versions 0.7.x may cause OOM errors.
- AMD (ROCm) support: FSDP + vLLM/SGLang works, but Megatron-LM backend is not yet available on ROCm.
- Advanced features in development: Async/off-policy training, full agent rollouts, and some multi-turn optimizations are on the roadmap (Q3 2025).
- Hardware assumption: Large-scale runs (e.g., 100B+ models) require multi-node, multi-GPU clusters—Verl is not optimized for single-GPU hobbyist use.
Summary
Verl represents a significant leap forward in RLHF infrastructure. By combining algorithmic flexibility, production-grade performance, and deep integration with the modern LLM ecosystem, it empowers researchers and engineers to run RLHF at scale without sacrificing speed, correctness, or extensibility. Backed by real-world deployments—from Doubao-1.5-Pro to AIME-champion models—and an active open-source community, Verl is quickly becoming the go-to framework for serious LLM alignment work.
If you’re building or aligning large language models and need an efficient, maintainable, and future-proof RLHF solution, Verl is worth adopting today.