If you’re building or evaluating text-to-image systems that demand both speed and visual fidelity, Decoupled DMD offers a breakthrough in few-step diffusion distillation. Unlike traditional approaches that treat distillation as a monolithic optimization problem, Decoupled DMD rethinks the mechanics behind fast image generation by decoupling two key components: CFG Augmentation (CA) as the driving engine and Distribution Matching (DM) as a stabilizing shield.
This insight powers Z-Image-Turbo, an 8-step image generator that ranks as the #1 open-source model on the Artificial Analysis Text-to-Image Leaderboard. With sub-second inference on enterprise GPUs and compatibility with consumer-grade hardware (≤16GB VRAM), Decoupled DMD enables real-world deployment of photorealistic, instruction-following image generation—without compromising quality for speed.
For engineers, product teams, and researchers prioritizing efficiency, scalability, and robustness in generative AI pipelines, Decoupled DMD provides both a practical tool (via Z-Image-Turbo) and a novel theoretical framework for designing next-generation distilled models.
Why Decoupled DMD Changes the Game
Beyond “Just Another Distillation Method”
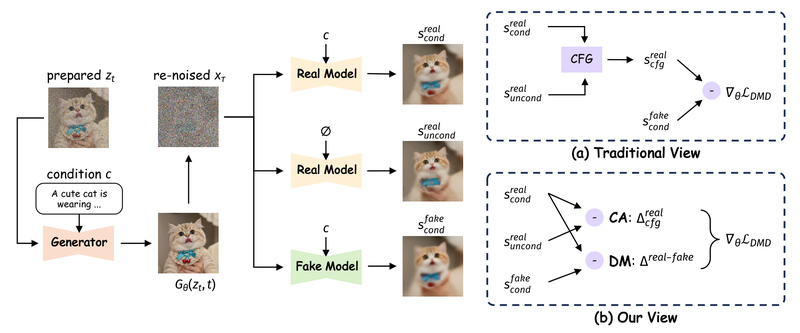
Most few-step distillation techniques, including earlier Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) variants, attribute their success to matching the output distribution of a teacher model. But Decoupled DMD reveals a more nuanced truth: in complex tasks like text-to-image generation—where Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) is essential for quality—the real performance driver is CFG Augmentation, not distribution matching itself.
- CFG Augmentation (CA) acts as the spear: it leverages diverse CFG conditions during training to expose the student model to a richer set of conditional generation scenarios, accelerating learning and enabling strong few-step performance.
- Distribution Matching (DM) serves as the shield: it regularizes training by aligning the student’s outputs with the teacher’s distribution, preventing mode collapse and reducing visual artifacts like blurring or structural inconsistencies.
Crucially, the paper demonstrates that DM is replaceable—simpler constraints or even GAN-style objectives can fulfill the same stabilizing role—while CA remains indispensable. This decoupling allows for modular optimization: you can tune or replace the “shield” without breaking the “engine.”
Practical Impact: The Z-Image-Turbo Advantage
The Z-Image project operationalizes Decoupled DMD to deliver Z-Image-Turbo, an 8-NFE (Number of Function Evaluations) model that:
- Generates 1024×1024 photorealistic images in under a second on H800 GPUs
- Runs efficiently on consumer GPUs with ≤16GB VRAM
- Supports accurate bilingual text rendering (English and Chinese)
- Exhibits strong instruction adherence, thanks to enhanced prompt understanding
These capabilities stem directly from the Decoupled DMD training process, which balances aggressive distillation (via CA) with stability (via DM), resulting in a model that is both fast and reliable.
When Should You Use Decoupled DMD?
Decoupled DMD isn’t a standalone library—it’s a training methodology—but its benefits are immediately accessible through the Z-Image model family. Consider adopting Z-Image-Turbo if your use case involves:
1. Low-Latency Image Generation APIs
Need sub-second response times for user-facing applications? Z-Image-Turbo’s 8-step inference eliminates the latency bottlenecks of 20–50 step pipelines while maintaining high visual quality.
2. Edge or Consumer Device Deployment
With support for CPU offloading and low VRAM usage (down to 4GB via third-party tools like stable-diffusion.cpp), Z-Image-Turbo enables high-quality generation on resource-constrained hardware.
3. Multilingual or Structured Text-to-Image Tasks
If your application requires rendering text within images—especially in both English and Chinese—Z-Image-Turbo’s training data and distillation process specifically optimize for this challenging capability.
4. Rapid Prototyping with Pre-Distilled Models
Rather than spending weeks distilling your own few-step model, you can start immediately with a battle-tested, leaderboard-ranked checkpoint that embodies Decoupled DMD’s principles.
How to Get Started
While Decoupled DMD itself is a research algorithm, you can leverage its benefits today through Z-Image-Turbo via Hugging Face and the diffusers library:
from diffusers import ZImagePipeline
import torch
pipe = ZImagePipeline.from_pretrained( "Tongyi-MAI/Z-Image-Turbo", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
pipe.to("cuda")
image = pipe( prompt="A neon-lit cyberpunk alley in Tokyo, rain-soaked streets, glowing signs in Japanese and English", height=1024, width=1024, num_inference_steps=9, # Results in 8 DiT forward passes guidance_scale=0.0, # Turbo models require CFG = 0 generator=torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(42),
).images[0]
Key practical notes:
- Use
guidance_scale=0.0—Turbo models are distilled for zero-CFG inference. - Install
diffusersfrom source (pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) to access Z-Image support. - Enable performance optimizations like FlashAttention-2/3 or model compilation for faster inference.
Additionally, the ecosystem includes tools like Cache-DiT (4× speedup via parallelism) and LeMiCa (training-free acceleration), further enhancing real-world usability.
Limitations and Considerations
Before integrating Decoupled DMD (via Z-Image) into your stack, keep these constraints in mind:
- Not a plug-and-play distillation library: Decoupled DMD is currently only available through pretrained Z-Image checkpoints, not as a reusable distillation framework.
- Fixed inference steps: Z-Image-Turbo is optimized for exactly 8 steps; deviating from this (e.g., using 4 or 16 steps) degrades quality.
- No CFG tuning: Since guidance_scale must be 0, you cannot adjust prompt adherence strength at inference time.
- Base model not yet public: Full fine-tuning or custom distillation requires the Z-Image-Base checkpoint, which is “to be released.”
These trade-offs are typical of highly optimized distilled models—but for teams prioritizing speed and out-of-the-box performance, they are often acceptable.
Summary
Decoupled DMD redefines few-step diffusion distillation by isolating the true engine of performance (CFG Augmentation) from its stabilizing mechanism (Distribution Matching). This insight has been validated at scale through Z-Image-Turbo, which delivers state-of-the-art, open-source image generation in just 8 steps—ideal for real-time applications, edge deployment, and multilingual use cases.
While not a general-purpose distillation toolkit, Decoupled DMD’s practical embodiment in Z-Image-Turbo offers immediate value to developers seeking high-quality, ultra-fast image generation without the overhead of custom distillation pipelines. If your project demands speed, efficiency, and photorealistic output, Decoupled DMD—via Z-Image—is a solution worth adopting today.